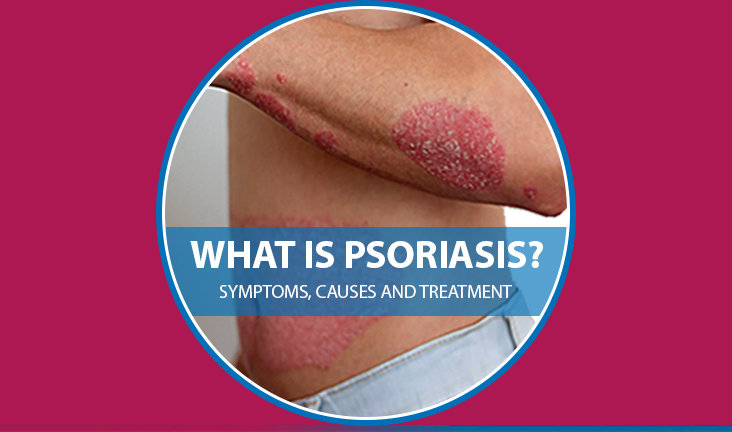
Psoriasis
Psoriasis affects millions of people around the world. This skin condition causes red, scaly patches on the skin. It is not contagious, but it can be very uncomfortable and affect a person’s quality of life. In this article, we will explore what psoriasis is, its causes, symptoms, and how to manage it.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease. This means it lasts for a long time and can come and go. Psoriasis sufferers have hyperactive immune systems. Skin cells expand too quickly as a result of this. Normally, skin cells take about a month to move from the deepest layer of the skin to the surface. In people with psoriasis, this process happens in just a few days. The fast turnover of skin cells leads to the build-up of thick, scaly patches on the skin.
Causes of Psoriasis
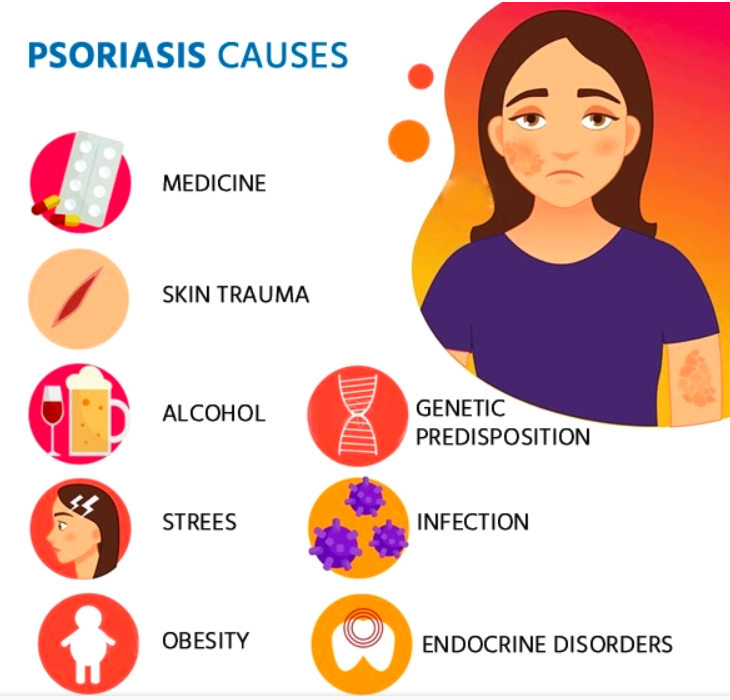
The exact cause of psoriasis is not known, but researchers believe several factors play a role:
- Genetics: Psoriasis runs in families. If one of your parents has psoriasis, you have a higher chance of developing it. If both of your parents have psoriasis, your risk is even higher.
- Immune System: In psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This causes the body to produce new skin cells more quickly than normal.
- Environmental Triggers: Certain factors can trigger psoriasis or make it worse. These include stress, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications.
Types of Psoriasis

There are several types of psoriasis, and each type looks different and affects different parts of the body.
Plaque Psoriasis: This is the most popular form. It causes red, inflamed patches covered with silvery-white scales. These patches can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp.
- Guttate Psoriasis: This type often starts in childhood or young adulthood. It looks like small, red spots on the skin. These spots usually appear on the torso, arms, and legs.
- Inverse Psoriasis: This type affects the skin folds, such as under the breasts, in the groin, or around the buttocks. It causes bright red, shiny patches that are smooth and not scaly.
- Pustular Psoriasis: This type causes white pustules (blisters of non-infectious pus) surrounded by red skin. It can occur on the hands and feet or cover most of the body.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: This is a rare and severe form of psoriasis. It causes widespread redness and can cover the entire body. It can be very painful and itchy and may require emergency medical treatment.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis symptoms might change based on the kind and severity of the ailment.
Common symptoms include:
- Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Itching, burning, or soreness
- Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails
- Stiffness and swollen joints (psoriatic arthritis patients)
How Doctors Diagnose Psoriasis
Doctors can usually diagnose psoriasis by examining the affected skin. They look at the size, shape, and location of the patches. Sometimes, they take a small sample of the skin (a biopsy) and examine it under a microscope. They can rule out other skin conditions via this.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
There is no cure for psoriasis, but several treatments can help manage the symptoms. Treatment depends on the type and severity of psoriasis and the patient’s response to previous treatments. Common treatments include:
- Topical Treatments: Doctors often prescribe creams and ointments to apply directly to the skin. These include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, and retinoids. These treatments can reduce inflammation and slow down the production of skin cells.
- Phototherapy: This treatment uses natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light. Doctors expose the skin to controlled amounts of UV light, which can reduce symptoms. Common types of phototherapy include UVB phototherapy and PUVA (psoralen combined with UVA light).
- Systemic Treatments: For more severe cases, doctors may prescribe oral or injected medications. These medications work throughout the body and include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics. Biologics target specific parts of the immune system and can be very effective.
- Lifestyle Changes: People with psoriasis can also benefit from lifestyle changes. Maintaining a healthy diet, reducing stress, avoiding smoking and alcohol, and keeping the skin moisturized can help manage symptoms.
Living with Psoriasis
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but many people find ways to manage the condition and live full, active lives. Here are some tips to help:
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations and take your medications as prescribed. This can help control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Take Care of Your Skin: Keep your skin moisturized to prevent dryness and cracking. Use gentle, fragrance-free products, and avoid harsh soaps and hot water.
- Manage Stress: Stress can trigger or worsen psoriasis. Engage in stress-relieving practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing. Frequent exercise can also aid in stress reduction.
- Connect with Others: Joining a support group or talking to others who have psoriasis can provide emotional support and practical advice. You are not alone, and sharing your experiences can be very helpful.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about psoriasis and stay up-to-date with new treatments and research. Making sensible choices regarding your care can be aided by this.
Common Myths About Psoriasis
There are many myths and misconceptions about psoriasis. Here are a few common ones:
- Myth 1: Psoriasis is contagious. This is not true. Psoriasis cannot be caught from another person.
- Myth 2: Only adults get psoriasis. Psoriasis can affect people of all ages, including children.
- Myth 3: Psoriasis is just a skin condition. Psoriasis is more than a skin condition. It is an autoimmune disease that can also affect the joints (psoriatic arthritis) and increase the risk of other health problems such as heart disease and diabetes.
- Myth 4: There is nothing you can do about psoriasis. While there is no cure, many treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for people with psoriasis.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex and challenging condition, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, people with psoriasis can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step in managing this condition. Always consult with a healthcare professional for the best advice and treatment plan for your specific situation. Stay informed, stay positive, and take control of your health.
Homeopathic Treatment for Psoriasis

Psoriasis is a long-term skin disorder characterized by red, scaly skin areas. While traditional medicine offers various treatments, some people seek alternative approaches like homeopathy. Homeopathy is a natural medical technique that stimulates the body’s healing mechanisms with greatly diluted chemicals. This article will explore how homeopathy can help manage psoriasis, the principles behind it, and some common homeopathic remedies for psoriasis.
Principles of Homeopathy
Homeopathy operates on the principle of “like cures like.” This means that substances that can cause symptoms in a healthy person can, in very small doses, treat similar symptoms in a sick person. Homeopaths also believe in individualizing treatment. They consider the patient’s overall physical and emotional condition, not just their specific symptoms. The preparation of homeopathic remedies involves a series of reductions and violent shaking, or succession.
How Homeopathy Treats Psoriasis
Homeopathy aims to treat the whole person, not just the symptoms. Homeopaths assess the patient’s physical, emotional, and mental health. They then select a remedy that matches the patient’s overall symptom picture. The goal is to stimulate the body’s natural healing ability and restore balance. Some people report improvements in their skin condition and overall well-being with homeopathic treatment.
Common Homeopathic Remedies for Psoriasis

Homeopathy offers several remedies for psoriasis, tailored to individual symptoms and overall health. Here are some frequently used remedies:
- Arsenicum Album: Used for dry, scaly skin with severe itching and burning, which improves with warmth. Suitable for anxious and restless individuals.
- Graphites: Ideal for thick, rough skin with deep cracks and a sticky discharge. These patients may have digestive issues and feel worse in cold weather.
- Sulphur: For red, inflamed skin with intense itching and burning that worsens with heat and washing. These individuals often crave sweets and spicy foods.
- Sepia: Helps with dry, itchy patches, especially in the bends of elbows and knees. Suitable for those feeling emotionally indifferent and fatigued.
- Calcarea Carbonica: Best for thick, scaly skin in overweight individuals who sweat easily and crave eggs and sweets. They feel worse in cold, damp conditions.
- Petroleum: Effective for rough, cracked skin on the hands that bleeds and itches intensely, particularly in winter. Also useful for thick crusts forming on the hands.
- Rhus Tox: Suitable for hard, rough, cracked skin on the back of hands, often spreading to the left arm. Also helps with joint inflammation, pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Mezereum: Treats eruptions that ooze sticky fluid and form crusts, sometimes with pus underneath. Provides relief from violent itching and burning in fluid-filled bumps.
- Malandrium: Used for deep cracks on the hands that worsen in winter, causing dry skin and intense itching, especially after washing.
- Sarsaparilla: Heals deep, painful cracks on the sides of fingers, making the skin hard. Also treats itchy, scaly spots on the hands.
- Anagallis: Useful for tiny fluid-filled bumps that ooze yellow-brown fluid when scratched, grouped vesicles, and dry eruptions on the hands and fingers.
- Antimonium Crudum: Effective for discolored, brittle, cracked, and deformed nails. Also beneficial for painful skin under the nails and inflamed finger joints.
The Process of Homeopathic Treatment
Homeopathic treatment for psoriasis begins with a detailed consultation. The homeopath asks about the patient’s symptoms, lifestyle, medical history, and emotional state. Based on this information, the homeopath selects a remedy that closely matches the patient’s overall symptom picture.
The remedies are usually in the form of small pellets or liquid drops. The patient takes the remedy according to the homeopath’s instructions. Follow-up appointments are important to assess progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment.
Safety and Efficacy of Homeopathy
Homeopathy is generally considered safe when practiced by a trained and experienced homeopath. The remedies are highly diluted and usually do not cause side effects. However, it’s important to note that scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of homeopathy for psoriasis is limited and controversial. Some studies suggest that homeopathy can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life, while others find no significant benefit
Integrating Homeopathy with Conventional Treatment
Many people use homeopathy alongside conventional treatments for psoriasis. It’s essential that you let your doctor know about any homeopathic treatments you use. This ensures that all aspects of your treatment are coordinated and that there are no potential interactions or conflicts between therapies.
Tips for Managing Psoriasis with Homeopathy
If you decide to try homeopathic treatment for psoriasis, consider the following tips:
- Consult a Qualified Homeopath: Choose a licensed and experienced homeopath. They can provide a comprehensive assessment and appropriate remedy selection.
- Be Patient: Homeopathic treatment can take time to show results. Consistent follow-ups with your homeopath are crucial for monitoring progress and adjusting the treatment as needed.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Complement homeopathic treatment with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques. These can help improve overall health and potentially reduce psoriasis flare-ups.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about psoriasis and its triggers. Understanding your condition can help you make informed decisions about your treatment options.
Conclusion
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing psoriasis. While scientific evidence on its efficacy remains mixed, many people find relief through individualized homeopathic treatment. If you are considering homeopathy for psoriasis, consult with a qualified homeopath and maintain open communication with your healthcare providers. By integrating homeopathic treatment with a healthy lifestyle and conventional medical care, you can take proactive steps towards managing your psoriasis and improving your quality of life.